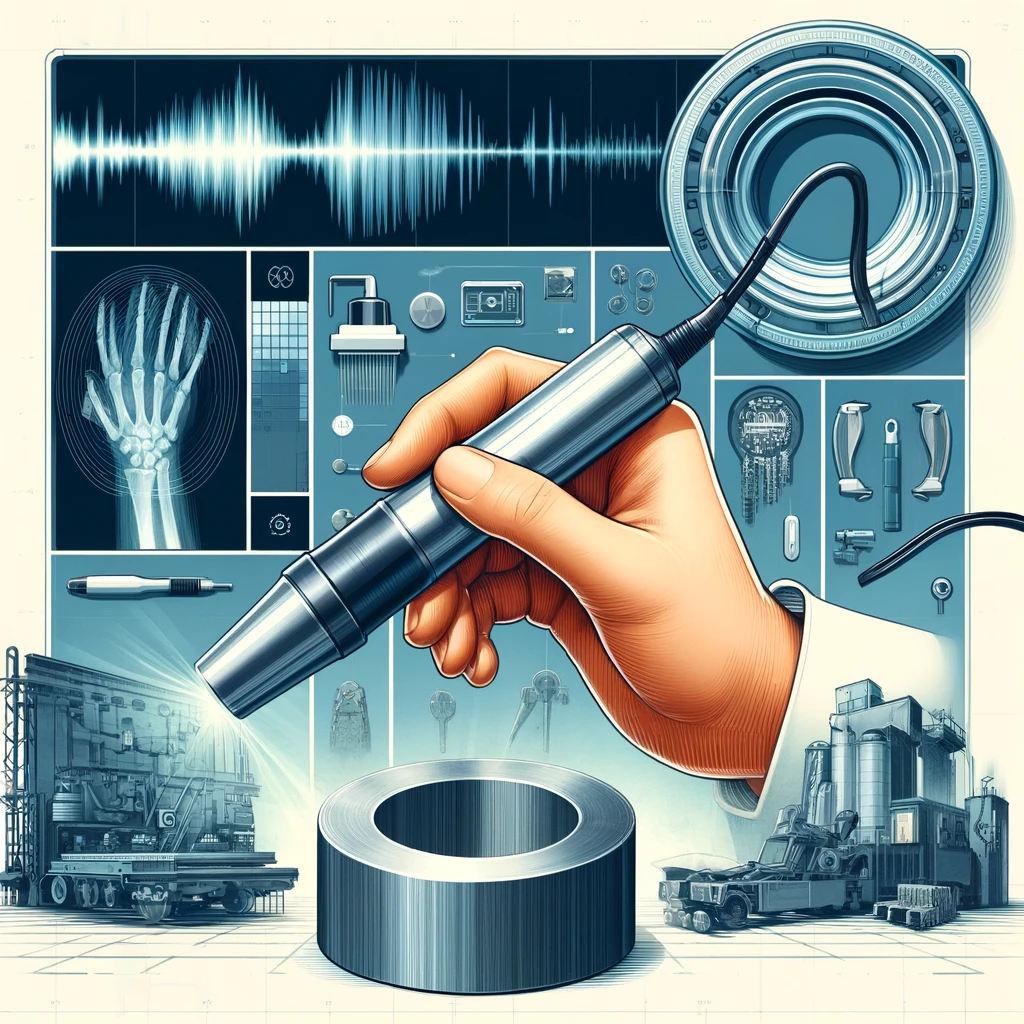
Introduction
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) is crucial for assessing component integrity in industries where safety and reliability are paramount. Governed by ISO 9712 standards, which ensure the qualification and certification of NDT personnel, these techniques allow for the thorough inspection of materials without causing damage. This article offers a detailed look at various NDT methods, providing foundational knowledge before delving into more specific applications.
The Importance of Non-Destructive Testing
NDT methods are indispensable in sectors such as aerospace, construction, manufacturing, and energy. These techniques help detect defects early, ensuring safety, compliance, and efficiency while preventing potential failures. Adhering to ISO 9712 helps standardize qualifications globally, ensuring consistent quality and safety standards across industries.

ISO 9712 Certification
ISO 9712 provides a framework for the certification of NDT personnel, promoting a standardized approach to training, examination, and certification. This international standard facilitates the mutual recognition of qualifications, supporting a consistent level of competency among NDT technicians worldwide.
Types of Non-Destructive Testing
Each NDT method offers unique advantages and is chosen based on material type, industry requirements, and the nature of the defects sought:
Visual Testing (VT): The simplest and most cost-effective form of NDT, VT involves a direct inspection of components using the naked eye or tools like magnifying glasses and cameras. It is particularly effective for surface examination and can detect irregularities such as cracks, alignment issues, and corrosion.

Penetrant Testing (PT): Ideal for detecting surface-breaking defects in non-porous materials, PT involves applying a visible or fluorescent dye to the clean surface. The dye penetrates the defects and is then drawn out by a developer, visibly highlighting any flaws under appropriate lighting conditions.

Magnetic Particle Testing (MT): This method is applicable for ferromagnetic materials and uses a magnetic field to detect surface and slightly subsurface discontinuities. Fine magnetic particles applied to the surface clump along flaws, visible directly or under ultraviolet light if a fluorescent particle is used.

Radiographic Testing (RT): RT provides a permanent film record and is highly effective for volumetric inspections. It uses penetrating X-rays or gamma rays to capture images of a material’s internal structure, revealing defects such as cracks, voids, and porosity.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): UT utilizes high-frequency sound waves that reflect from flaws and interfaces within a material. It is highly effective for detecting internal defects and can also provide measurements of material thickness and characterization.
Conclusion
Non-Destructive Testing is a key practice in maintaining the highest standards of safety and quality in manufacturing and construction. Understanding the various NDT methods under ISO 9712 ensures that professionals are well-prepared to apply these techniques effectively. Stay tuned for our detailed exploration of each NDT method in our upcoming articles.
Contact Us
For expert NDT services certified under ISO 9712, reach out to Smart Consulting & Inpection. Our experienced team is equipped to ensure the integrity and safety of your critical components with precision and expertise.