The 2014/34/EU Directive, known as the ATEX Directive, is a crucial regulation within the European Union. It governs the use of equipment and protective systems in potentially explosive atmospheres. This directive ensures that all equipment used in such environments meets strict safety and health standards. Thus, it helps prevent accidents and protects lives.
What is the ATEX Directive?

The ATEX Directive, named after the French term “Atmosphères Explosibles,” sets the legal framework for making, distributing, and using equipment in explosive atmospheres. An explosive atmosphere exists when a mixture of air, flammable substances (in the form of gases, vapors, mists, or dust), and a source of ignition can cause an explosion.
The directive has two main parts:
- ATEX 2014/34/EU: This part applies to manufacturers. It covers the requirements for equipment and protective systems intended for use in explosive atmospheres.
- ATEX 1999/92/EC: This part applies to employers. It covers the minimum requirements for improving the safety and health protection of workers potentially at risk from explosive atmospheres.
Scope of the ATEX Directive
The 2014/34/EU ATEX Directive applies to a wide range of products, including:
- Electrical and non-electrical equipment
- Protective systems
- Components for use in equipment or protective systems
- Safety devices, control devices, and regulating devices used outside the explosive atmosphere but essential for safe functioning
Requirements for Compliance
To comply with the ATEX Directive, manufacturers must ensure their products meet essential health and safety requirements. These include:
- Design and Construction: Equipment must prevent the ignition of explosive atmospheres.
- Materials: Use suitable materials to prevent interactions that could lead to explosions.
- Safety Devices: Implement devices to control or shut down operations in hazardous situations.
- Marking and Instructions: Clearly mark equipment with safety information and provide comprehensive instructions for safe use.

Certification Process
Certification is a critical aspect of the ATEX Directive. Manufacturers must test and assess equipment rigorously to ensure compliance with the directive’s standards. The certification process involves several steps:
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential ignition sources and assess the risk of explosion.
- Design and Testing: Design equipment to reduce identified risks and test it under various conditions.
- Documentation: Compile technical documents detailing compliance with ATEX requirements.
- Notified Bodies: Work with notified bodies—independent organizations authorized to evaluate and certify equipment for ATEX compliance.
Role of Notified Bodies
Notified bodies play a crucial role in the ATEX certification process. These organizations, designated by EU member states, assess the conformity of equipment with the ATEX Directive. They conduct rigorous evaluations, including:
- Product Testing: Verify that equipment meets safety standards through tests.
- Quality Assurance: Audit manufacturers’ quality systems to ensure consistent production of compliant equipment.
- Certification: Issue ATEX certificates confirming the equipment’s compliance with the directive.
Marking and Identification
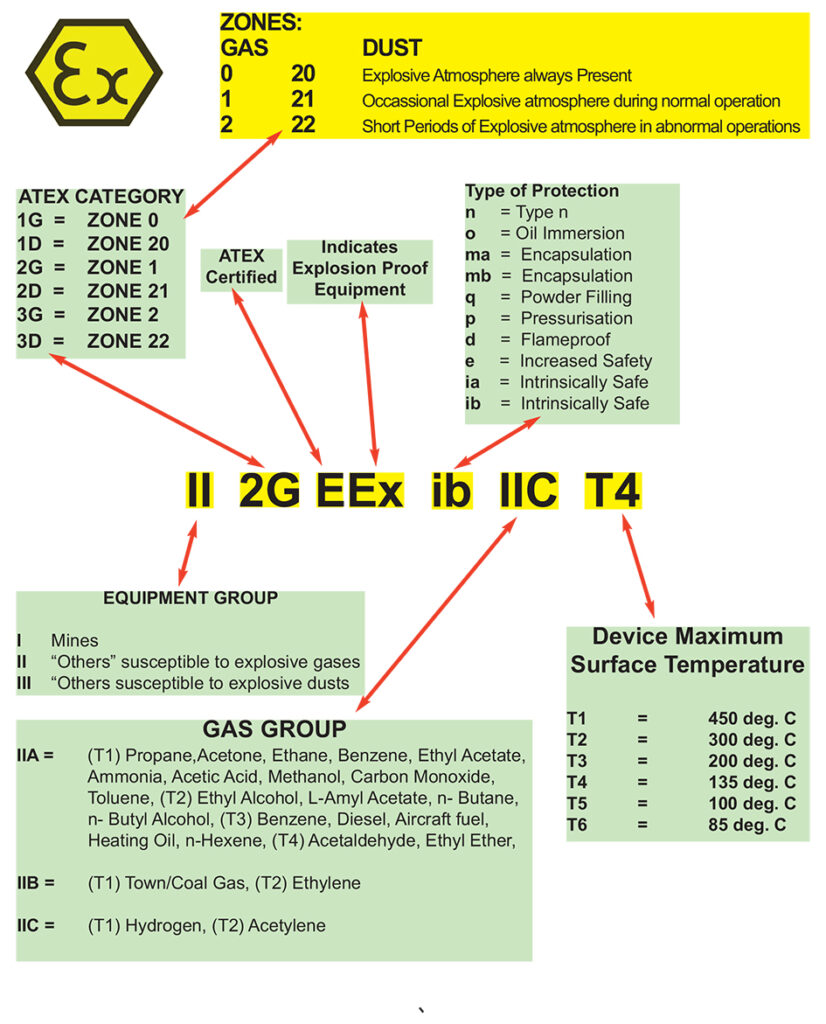
ATEX-compliant equipment must have specific markings to indicate its suitability for use in explosive atmospheres. Understanding these markings is essential for ensuring proper use and safety. For example, consider the following ATEX code: II 2G EEx ib IIC T4. Here’s how to read it:
- II: Indicates the equipment group. Group II is for equipment intended for use in all explosive atmospheres except mines susceptible to firedamp (Group I).
- 2G: Indicates the equipment category and type of explosive atmosphere. “2” signifies high protection level for areas where explosive atmospheres are likely to occur. “G” indicates gas.
- EEx: Denotes that the equipment conforms to European standards for explosion protection.
- ib: Indicates the type of protection method used. “ib” refers to intrinsic safety, where the equipment is designed to be safe under both normal and fault conditions.
- IIC: Specifies the gas group. “IIC” covers the most explosive gas environments, including hydrogen and acetylene.
- T4: Indicates the temperature class, with T4 meaning the equipment’s surface temperature will not exceed 135°C.
Employer Responsibilities under ATEX 1999/92/EC
The ATEX 1999/92/EC directive places obligations on employers to protect workers from explosive atmospheres. Employers must:
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Identify and assess the risk of explosion in the workplace.
- Implement Control Measures: Use equipment and protective systems that comply with ATEX standards.
- Provide Training: Ensure workers are trained in explosion prevention and safety procedures.
- Maintain Documentation: Keep records of risk assessments, control measures, and equipment maintenance.
Conclusion
The 2014/34/EU ATEX Directive is essential for ensuring the safety of equipment used in explosive atmospheres. Compliance with this directive involves rigorous design, testing, and certification processes to meet stringent safety standards. By adhering to ATEX requirements, manufacturers and employers can significantly reduce the risk of explosions, protecting both workers and facilities.
Contact Us
For more information about ATEX compliance and how to ensure your equipment meets the 2014/34/EU Directive standards, contact SMART Consulting & Inspection. Our experts are ready to assist you with comprehensive compliance solutions and certification support.


